Pleurocentesis, also called thoracentesis, is a medical procedure. It removes excess fluid from the pleural space. This space lies between the lungs and chest wall. Fluid buildup here causes breathing problems and chest pain. Doctors perform pleurocentesis to ease symptoms and diagnose conditions.
Pleural effusion occurs due to several reasons. These include infections, heart failure, cancer, or injury. If untreated, fluid can compress the lungs. That leads to shortness of breath and discomfort. Pleurocentesis helps patients breathe easier and allows analysis of the fluid.
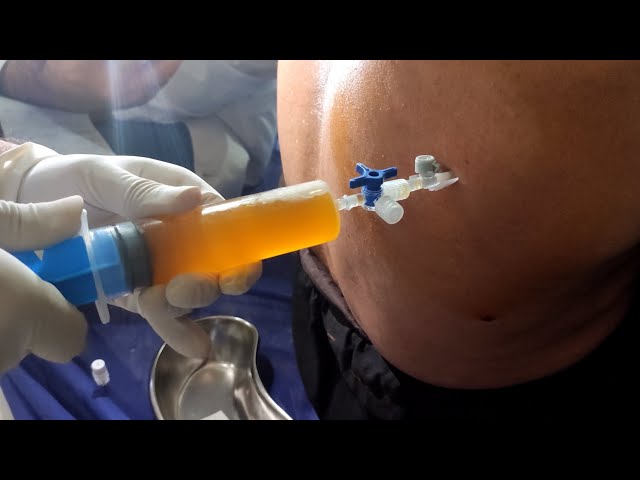
Doctors begin by identifying the fluid’s location using imaging. Ultrasound or X-rays guide them. The patient sits upright during the procedure. After sterilizing the area, local anesthesia is applied. A thin needle or catheter is inserted into the pleural cavity. Fluid is gently withdrawn into a syringe or bag.
These symptoms often indicate pleural effusion. Medical evaluation confirms the diagnosis before the procedure.
The collected fluid undergoes laboratory tests. Analysis reveals infections like tuberculosis or pneumonia. It can also detect cancer cells, blood, or pus. Protein and glucose levels help determine the cause. Accurate diagnosis ensures effective treatment.
The benefits outweigh the risks when performed correctly.
Though generally safe, pleurocentesis has some risks. These include:
Doctors minimize these risks using sterile techniques and imaging guidance.
Patients are observed for a few hours post-procedure. A chest X-ray checks for complications. Most people return to normal activities within a day. Pain is minimal and managed with over-the-counter medications.
Managing the root cause prevents fluid buildup. For instance, treating heart failure or infections reduces recurrence. In some cases, repeat pleurocentesis or pleurodesis may be necessary. Lifestyle changes and regular follow-ups help maintain lung health.
If you experience breathing issues or chest discomfort, seek medical advice. Early detection prevents complications. Your doctor will guide you on imaging tests and treatment options.
Pleurocentesis is a vital procedure for diagnosing and treating pleural effusion. It offers quick relief and critical diagnostic insight. With low risk and high success rates, it remains a key tool in modern medicine.
Copyright © All Rights Reserved, By Dr. Harsh Vij